Loading...
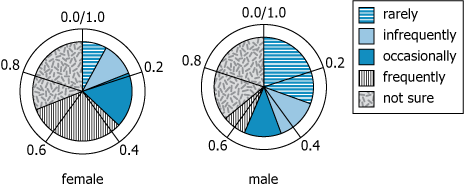
The two charts show how female and male survey respondents answered a question about how often they ate a certain type of food. The survey specified that "infrequently" meant more often than "rarely" but less often than "occasionally."
Select from the drop-down menus the options that create the statement that most accurately reflects the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Survey Subject | "how female and male survey respondents answered a question about how often they ate a certain type of food" | The dataset records how often men and women report eating a specific food. |
| Frequency Definition | "The survey specified that 'infrequently' meant more often than 'rarely' but less often than 'occasionally.'" | The key frequency options are in order: rarely < infrequently < occasionally. |
| Chart Component | What's Shown | What This Tells Us |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Two side-by-side polar pie charts (female on left, male on right) | Enables visual comparison of male and female survey responses. |
| Categories | rarely, infrequently, occasionally, frequently, not sure | Survey participants had five options to describe eating frequency, including uncertainty (not sure). |
| Gender Differences | Female: rarely 9.5%, infrequently 9.5%, occasionally 19%, frequently 31%, not sure 31% Male: rarely 32%, infrequently 12%, occasionally 12%, frequently 8%, not sure 36% |
Males more likely to report rarely/infrequently; females more distributed, with higher frequent consumption. |
| Not sure responses | Females: 31%, Males: 36% | Large percentages in both groups were unsure. |
Slightly less than [BLANK 1] respondents indicated that they ate the food at most [BLANK 2].
Slightly less than 20% of the female respondents indicated that they ate the food at most [BLANK 2].
By summing 'rarely' and 'infrequently' for females (\(\mathrm{9.5\% + 9.5\% = 19\%}\)), we see this is slightly less than 20%. Thus, '20% of the female' and 'infrequently' are the answers for the blanks in the statement.
The blanks are not independent: the correct choice for the first blank (gender and percentage) depends on which frequency level is chosen for the second blank, because the cumulative percentages differ by gender and frequency.