Loading...
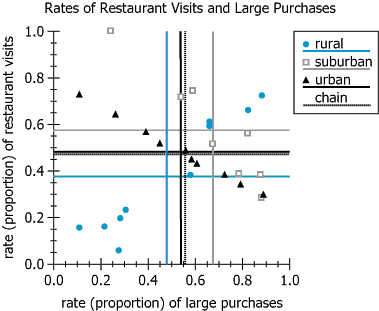
The PQ&R Café and Grocery is a chain of small grocery stores with restaurants. The locations are grouped by type of area—rural, urban, and suburban. PQ&R collected data from all 28 of its locations on the rate of restaurant visits among its customers and the rate of large purchases in the grocery section. The results are presented in the graph. The average (arithmetic mean) rates for each group as well as the chain-wide average are represented by the horizontal and vertical lines.
Use the drop-down menus to fill in the blanks in each of the following statements based on the information given by the graph.
| Text Component | Content | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Business Overview | The PQ&R Café and Grocery is a chain of small grocery stores with restaurants. | The company operates grocery stores that also serve meals. |
| Location Grouping | The locations are grouped by type of area—rural, urban, and suburban. | Each store is classified into one of three geographic area types. |
| Dataset Scope | PQ&R collected data from all 28 of its locations. | The dataset includes every location in the chain \((n=28)\). |
| Measured Variables | Rate of restaurant visits among its customers; rate of large purchases in the grocery section. | Each store is evaluated by two proportions: visits and purchases. |
| Graph Annotation | Average rates for each group and the chain-wide average shown by horizontal and vertical lines. | The graph includes reference lines for group and overall averages. |
| Chart Component | Contents/Features | Analysis/Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Plot Type | Scatter plot with four series | Compares two variables across distinct location types |
| X-axis | Rate of large grocery purchases \((0.0 \text{ to } 1.0)\) | Left/right position = proportion of customers with large purchases |
| Y-axis | Rate of restaurant visits \((0.0 \text{ to } 1.0)\) | Up/down position = proportion of customers visiting the restaurant |
| Series | Rural (blue circle), Suburban (empty square), Urban (black triangle), Chain average (filled triangle) | Data grouped visually by location type and chain averages |
| Reference Lines | Horizontal at \(y ≈ 0.35\) and \(y ≈ 0.45\), vertical at \(x ≈ 0.5\) | Show group and chain-wide means, segmenting the chart into quadrants |
| Distribution | Rural clustered low (lower left), suburban mainly right of vertical | Rural sites have generally low rates both metrics; suburban have higher large purchases |
| Trend | Suburban points show no clear directional trend | Implies no strong suburban correlation between the two variables |
Suburban locations have the highest average rate of large purchases, as most of their points are to the right of the chain-wide average vertical line \((x ≈ 0.5)\). Rural locations cluster in the lower left, having low rates for both restaurant visits and large grocery purchases. Suburban locations' points show no clear trend, indicating little or no correlation between large purchases and restaurant visits for this group.
Among suburban locations, there is a [BLANK] correlation between the rate of large purchases and the rate of restaurant visits.
The average rate of large purchases is greatest for [BLANK] locations.
By examining the arrangement of suburban locations on the scatter plot, we determined that there is a strongly negative correlation between large purchases and restaurant visits for suburban areas. Looking at the group averages (vertical lines), suburban locations have the highest average rate of large purchases compared to urban and rural areas.
Question 1 and Question 2 are independent. The first requires analyzing directionality among suburban points, while the second is a comparison of group averages. Neither solution depends on knowing the answer to the other.