Loading...
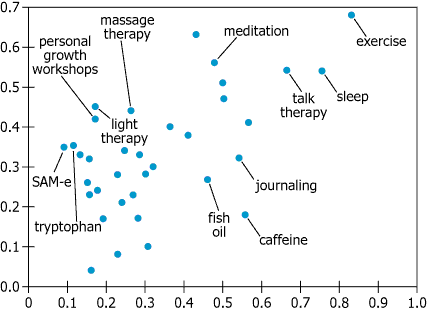
The graphic displays results of an Internet survey on the effectiveness and popularity of various treatments for depression. The scale on the horizontal axis represents popularity, \(\mathrm{P}\), defined as the fraction of all respondents who tried the treatment; the scale on the vertical axis represents effectiveness, \(\mathrm{F}\), defined as the fraction of all respondents who considered a given treatment to be effective.
On the basis of the information provided, select from each of the drop-down menus the option that creates the most accurate statement.
| Component | Content |
|---|---|
| Data Source | Internet survey results |
| Subject | Variety of depression treatments |
| X-axis (P) | Popularity: Fraction of all respondents who tried the treatment \(\mathrm{(values\ 0\ to\ 1.0)}\) |
| Y-axis (F) | Effectiveness: Fraction of all respondents who considered a treatment effective \(\mathrm{(0\ to\ 0.7)}\) |
| Labels Noted | 12 labeled treatments (e.g., exercise, caffeine, sleep, talk therapy, etc.) |
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Scatter plot (~30-35 blue dots) |
| Axes | X-axis: Popularity \(\mathrm{(0\ to\ 1.0)}\), Y-axis: Effectiveness \(\mathrm{(0\ to\ 0.7)}\) |
| Labels | 12 explicitly labeled treatments incl. exercise, caffeine, sleep, talk therapy, etc. |
| Prominent Pattern | Exercise: furthest right and highest dot, denoting most popular and most effective |
| Caffeine Position | Among most popular \(\mathrm{(P \gt 0.5)}\), but lowest on effectiveness axis |
| Distribution | Most labeled treatments with moderate to high popularity have mid-to-upper effectiveness |
The treatment that was both the most effective and used by the greatest number of people is ______.
Among the labeled treatments tried by more than half of the respondents, ______ was the least effective.
By visually inspecting the scatter plot, we see that 'exercise' achieves both the highest popularity and effectiveness, making it the correct answer for the first blank. For the second blank, among treatments with popularity greater than 0.5, 'caffeine' stands out as the least effective, even though it is widely tried. This method relies on finding where points are positioned on the plot relative to the X and Y axes without needing numerical calculations.
Each question can be solved independently since the first asks for the best overall in both popularity and effectiveness, while the second is restricted to the least effective among only the popular treatments. The answer to one does not affect the other.