Owning the Dataset
Table 1: Text Analysis
| Text Component |
Content |
Interpretation |
| Data Scope |
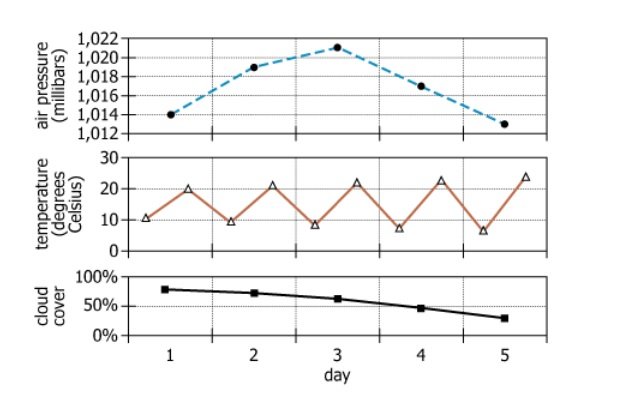
Three data sets from a 5-day weather forecast |
3 different weather variables measured across 5 days |
| Location |
For a certain city |
All data comes from a single, unspecified city |
| Variable 1 |
Daily average air pressure |
The average air pressure recorded each day |
| Variable 2 |
Daily high and low temperatures |
Both maximum and minimum temperature values for each day |
| Variable 3 |
Daily average percentage of cloud cover |
The daily average of cloud cover, expressed as a percent |
Table 2: Chart Analysis
| Chart Component |
Description |
Interpretation |
| Chart Layout |
Three vertically stacked line charts, same x-axis (Day 1 to Day 5) |
Easily compare trends by day for all variables |
| Air Pressure |
Blue dashed line, ranges from \\(\\sim 1.012\\) to \\(\\sim 1.022\\) millibars, peaks at Day 3 |
Inverted U-shaped: rises through Day 3, then falls |
| Temperature |
Orange line with triangular markers, zigzag pattern between \\(\\sim 10°\mathrm{C}\\) (low) and \\(\\sim 20°\mathrm{C}\\) (high) |
Alternating daily highs and lows, consistent amplitude |
| Cloud Cover |
Black line with square markers, steady decline from near 100% to below 50% over 5 days |
Persistent decrease in cloudiness, no reversals |
| General Trend Summary |
Air pressure: single peak; Temperature: regular oscillation; Cloud cover: continuous decrease |
Patterns make visual relationships and potential correlations clear |
Key Insights
- Each dataset represents a distinct weather variable (air pressure, temperature, cloud cover) measured daily across 5 days for a single city.
- Air pressure exhibits a single-peak, inverted U-shape: it increases to Day 3, then decreases.
- Temperature shows a regular zigzag pattern, alternating daily highs (\\(\\sim 20°\mathrm{C}\\)) and lows (\\(\\sim 10°\mathrm{C}\\)), with consistent amplitude.
- Cloud cover has a steady, monotonic decline from nearly 100% to below 50% over the 5 days, the most consistent trend among the three variables.
Step-by-Step Solution
Question 1: Determining which variable is most strongly negatively correlated
Complete Statement:
Among the three data sets shown in the graphs, the values for [BLANK 1] would be most strongly negatively correlated with a data set consisting of the 5 [BLANK 2] of the daily values shown for temperature.
Breaking Down the Statement
• Statement Breakdown 1:
- Key Phrase: Among the three data sets shown in the graphs
_ Meaning: We need to consider all three variables in the given charts: air pressure, temperature, and cloud cover.
_ Relation to Chart: There are three charts, each for a different variable collected over time.
_ Important Implications: Focus on variables other than temperature, since temperature is already specified in the question.
• Statement Breakdown 2:
- Key Phrase: most strongly negatively correlated
_ Meaning: Negative correlation means as one variable increases, the other decreases.
_ Relation to Chart: Look for variables whose trends move in opposite directions compared to temperature.
_ Important Implications: The variable we seek should go down as the relevant aspect of temperature goes up, or vice versa.
• What is needed: Which variable, air pressure or cloud cover, is most strongly negatively correlated with a specific feature of temperature.
Solution:
- Condensed Solution Implementation:
Examine each variable's trend for consistency and compare it to temperature's daily variations.
- Necessary Data points:
Cloud cover decreases steadily over the days. Air pressure rises then falls. Temperature oscillates between high and low each day.
_ Calculations Estimations:
Cloud cover exhibits a clear and steady decline, which can correlate in a predictable way with temperature. Air pressure changes pattern midweek.
_ Comparison to Answer Choices:
Cloud cover is the variable whose pattern is most likely to be negatively correlated with temperature's daily range since its trend is consistent.
FINAL ANSWER Blank 1: daily average percentage of cloud cover
Question 2: Determining which aspect of temperature is being compared
Complete Statement:
Among the three data sets shown in the graphs, the values for daily average percentage of cloud cover would be most strongly negatively correlated with a data set consisting of the 5 [BLANK 2] of the daily values shown for temperature.
Breaking Down the Statement
• Statement Breakdown 1:
- Key Phrase: the 5 [BLANK 2] of the daily values shown for temperature
_ Meaning: We must specify which measurement of temperature (such as means, minimums, or ranges) to use for the comparison.
_ Relation to Chart: Temperature alternates between high and low values each day, allowing calculation of a 'range' per day.
• Statement Breakdown 2:
- Key Phrase: negatively correlated with cloud cover
_ Meaning: As cloud cover decreases, the chosen measure of temperature should increase.
_ Relation to Chart: On days with less cloud cover, the temperature's daily high and low spread out farther.
• What is needed: What daily temperature measure (mean, minimum, range) increases as cloud cover decreases.
Solution:
- Condensed Solution Implementation:
Recall that lower cloud cover leads to warmer days and cooler nights, thus a greater daily range in temperature.
- Necessary Data points:
Cloud cover goes down. Temperature pattern shows significant day/night differences.
_ Calculations Estimations:
With fewer clouds, solar energy more easily heats the daytime and releases heat at night, increasing the high-low temperature difference.
_ Comparison to Answer Choices:
Only daily 'ranges' of temperature will systematically increase as cloud cover steadily declines.
FINAL ANSWER Blank 2: ranges
Summary
Cloud cover steadily decreases throughout the observed days, while daily temperature varies significantly between highs and lows each day. Less cloud cover results in clearer skies, which amplifies the difference between daytime highs and nighttime lows, thus increasing the daily temperature range. Therefore, the daily average percentage of cloud cover is most strongly negatively correlated with the daily ranges in temperature.
Question Independence Analysis
The blanks are dependent: the temperature measure in Blank 2 (ranges) is only relevant once Blank 1 (cloud cover) is identified, as it is the variable whose changes most strongly relate to temperature's day-to-night differences.