Loading...
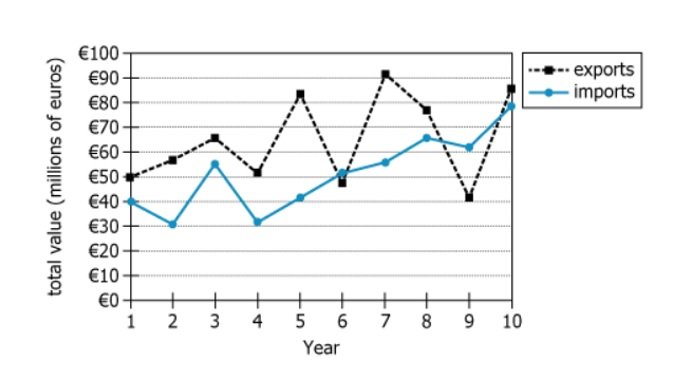
The graph shows the total value of Country X's exports to Country Y and the total value of Country X's imports from Country Y for each of 10 years.
Based on the information provided, select from each drop-down menu the option that creates the most accurate statement.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Subject Matter | total value of Country X's exports to Country Y and imports from Country Y | Examines trade flows between two countries |
| Geographic Context | Country X, Country Y | Specific but unnamed countries involved |
| Variables Tracked | exports, imports | Tracks both outgoing and incoming goods/services |
| Time Frame | for each of 10 years | Covers a decade of yearly data |
| Measurement Units | total value | Focuses on monetary worth, not quantities or types |
| Chart Element | What is Displayed | Observations and Interpretations |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Dual line graph: one series dashed (exports), one series solid (imports) | Enables direct year-by-year comparison |
| Value Range (Y-axis) | \(€10\text{ million}\) to \(€100\text{ million}\) | All data points fall within this range |
| Exports Line | Black dashed, fluctuates between \(€41\text{m}\) and \(€91\text{m}\) | Exports are more variable, with sharp increases/decreases |
| Imports Line | Blue solid, ranges from \(€30\text{m}\) to \(€79\text{m}\) | Imports are more stable, gradual changes |
| Intersecting Points | Lines cross at Year 6 and Year 9 | Only these years had imports exceed exports |
In Year [BLANK] the total value of Country X's imports from Country Y exceeded the total value of Country X's exports to Country Y.
by [BLANK] million euros, to the nearest 10 million euros.
By analyzing the years when imports exceed exports (years 6 and 9), and calculating the difference, only year 9 yields a difference (20 million euros) that matches the answer choices. Thus, year 9 and 20 million euros are the correct responses.
The two blanks are not independent: while there are multiple years when imports exceed exports, only one of them yields a difference that matches the answer choices for the second blank. Therefore, the answers are dependent on each other.