Loading...
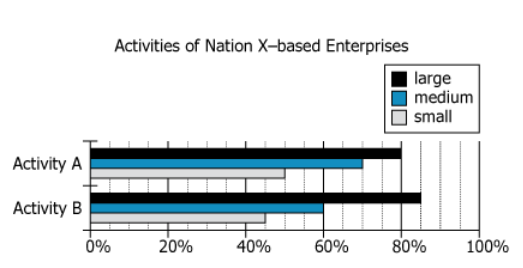
The graph shows the percentage of Nation X-based enterprises engaged in two international business activities: A and B. For the purposes of the graph, the enterprises are grouped by size (the number of employees each has)-large, medium, or small.
Based on the information provided, select from each drop-down menu the option that creates the most accurate statement.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Subject Matter | percentage of Nation X-based enterprises engaged in two international business activities: A and B | This dataset covers how often companies in Nation X participate in two specific international business activities |
| Grouping Method | enterprises are grouped by size (the number of employees each has) | Companies are classified as large, medium, or small by employee number |
| Size Categories | large, medium, or small | Three groups: large, medium, small enterprises |
| Measurement | percentage of enterprises engaged in activities | The proportion of enterprises within each size group that engage in each activity |
| Chart Component | What's Shown | What It Implies |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Horizontal 100% stacked bar chart (with 2 rows/activities) | Each activity visualizes its engaged enterprises by company size composition |
| Activities | Activity A (top bar), Activity B (bottom bar) | Direct comparison of the two activities |
| Segments | Each bar: black (large), cyan (medium), white (small) | Shows relative contribution by company size for each activity |
| Axis & Gridlines | 0-100% on X-axis, 20% intervals | Bar length reflects composition within activity, not engagement rate within size class |
| Notable Visual | Small (white) segment almost disappears for Activity B | Very low representation of small enterprises among those engaged in Activity B |
| Relation to Table | Chart shows composition per activity, not engagement rates | May cause confusion if misread as rates; need table data for actual engagement percentages |
In Nation X, a randomly selected [BLANK 1] enterprise is about [BLANK 2]% more likely to engage in Activity B than to engage in Activity A.
What is needed: Which enterprise size is more likely to engage in Activity B than Activity A (i.e., which has Activity B > Activity A).
In Nation X, a randomly selected Large enterprise is about [BLANK 2]% more likely to engage in Activity B than to engage in Activity A.
What is needed: By what percentage are Large enterprises more likely to engage in Activity B compared to Activity A?
Large enterprises are the only group more likely to engage in Activity B than A, with a relative likelihood of \(6.3\%\). Calculation involved comparing the rates for each size type and selecting the one with a positive result, then computing the percentage increase for that specific size.
The two blanks are dependent: you must first determine which enterprise size (Blank 1) qualifies, then calculate the percentage (Blank 2) for that specific size. If you choose a different size for Blank 1, the calculation for Blank 2 changes.