Owning The Dataset
Table 1: Text Analysis
| Text Component |
Literal Content |
Simple Interpretation |
| Subject Statement |
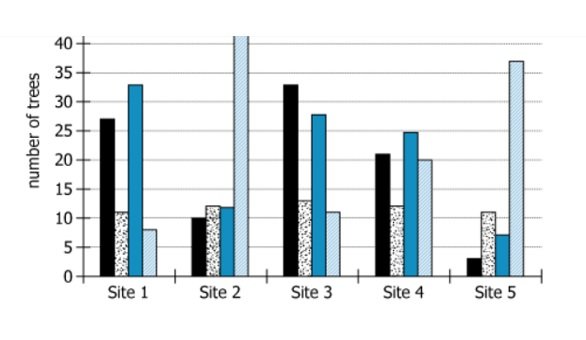
The graph shows the number of coniferous trees of each of 4 species |
Data is tree counts for 4 conifer species |
| Location Detail |
at each of 5 sites located in a large ecological reserve |
Data is taken from 5 different places in one large reserve |
| Species Legend |
Black: W, Dotted White: X, Blue: Y, Sky Blue: Z |
Four species: W, X, Y, and Z, each with its own color/pattern |
Table 2: Chart Analysis
| Chart Component |
Description |
Interpretation |
| Chart Type |
Grouped bar chart (species by site) |
Allows visual comparison of species at each site |
| X-Axis |
5 Sites (labeled 1 to 5) |
Each site is a distinct row/group |
| Y-Axis |
Number of trees (vertical; ranges from 0 to about 40) |
Indicates tree abundance per species per site |
| Series (bars/colors) |
4 series: W (Black), X (Dotted White), Y (Blue), Z (Sky Blue) |
Each color/pattern = 1 species |
| Notable Patterns |
X is almost unchanged; W and Y rise and fall together; W and Z rise/fall oppositely |
Indicates stability/correlation/anti-correlation among certain species |
Key Insights
Species X remains almost the same at every site, indicating low or no correlation with changes in other species. Species W and Y show a strong positive correlation: wherever W is numerous, Y is also numerous, and when W is scarce, so is Y. In contrast, Species W and Z have a strong negative correlation: W's population is high wherever Z's is low and vice versa. This suggests W and Z may respond oppositely to the same site conditions or compete with each other.
Step-by-Step Solution
Question 1: Identify the Strongest Positive Correlation with Species W
Complete Statement:
Comparing the total number of Species W trees at a site to the number of Species X, Y, and Z trees at that site, the graph shows the strongest positive correlation between the number of Species W and Species ______ trees
Breaking Down the Statement
- Statement Breakdown 1:
- Key Phrase: Comparing the total number of Species W trees at a site
- Meaning: Focus on the number of Species W trees across the different sites.
- Relation to Chart: These are most likely represented as a specific bar (e.g., black or labeled 'W') at each site on the bar chart.
- Important Implications: Species W is the reference species for correlation comparisons.
- Statement Breakdown 2:
- Key Phrase: to the number of Species X, Y, and Z trees at that site
- Meaning: Compare the numbers for each of the other three species at each site with Species W.
- Relation to Chart: These species are also represented as bars at each site, possibly with different colors or hatchings.
- Important Implications: Must consider each species in relation to W separately.
- What is needed: Which species (X, Y, or Z) shows a trend most similar to W's across all sites.
Solution:
- Condensed Solution Implementation:
Systematically check values for W against X, Y, and Z at each site, looking for a species that increases when W increases and decreases when W decreases.
- Necessary Data points:
Species counts for W, X, Y, and Z at all five sites:
- Site 1: \(\mathrm{W=27}\), \(\mathrm{X=11}\), \(\mathrm{Y=33}\), \(\mathrm{Z=8}\)
- Site 2: \(\mathrm{W=11}\), \(\mathrm{X=12}\), \(\mathrm{Y=41}\), \(\mathrm{Z=1}\)
- Site 3: \(\mathrm{W=33}\), \(\mathrm{X=12}\), \(\mathrm{Y=28}\), \(\mathrm{Z=11}\)
- Site 4: \(\mathrm{W=21}\), \(\mathrm{X=12}\), \(\mathrm{Y=25}\), \(\mathrm{Z=20}\)
- Site 5: \(\mathrm{W=3}\), \(\mathrm{X=11}\), \(\mathrm{Y=7}\), \(\mathrm{Z=37}\)
- Calculations Estimations:
Y is high when W is high (Site 1: \(\mathrm{W=27}\), \(\mathrm{Y=33}\); Site 3: \(\mathrm{W=33}\), \(\mathrm{Y=28}\)), and low when W is low (Site 5: \(\mathrm{W=3}\), \(\mathrm{Y=7}\)). X stays nearly the same at all sites. Z is highest where W is lowest (opposite trend).
- Comparison to Answer Choices:
X shows little to no correlation. Y shows a positive trend with W, except for one outlier (Site 2). Z shows the opposite trend. Therefore, Y is the correct choice for strongest positive correlation.
FINAL ANSWER Blank 1: Y
Question 2: Identify the Strongest Negative Correlation with Species W
Complete Statement:
...and the strongest negative correlation between the number of Species W and Species ______ trees
Breaking Down the Statement
- Statement Breakdown 1:
- Key Phrase: strongest negative correlation
- Meaning: A strong negative correlation means as W increases, another species decreases (and vice versa).
- Relation to Chart: Look for bars with opposite highs/lows compared to W.
- Statement Breakdown 2:
- Key Phrase: the number of Species W and Species ______ trees
- Meaning: We are comparing W to each of the other species to determine which one is most strongly inversely related.
- Relation to Chart: Compare the W bar at each site to the X, Y, and Z bars.
- What is needed: Which species (X, Y, or Z) is most consistently high when W is low, and low when W is high.
Solution:
- Condensed Solution Implementation:
Analyze how the numbers for X, Y, and Z change in response to changes in W across sites.
- Necessary Data points:
Relevant species counts:
- Site 1: \(\mathrm{W=27}\), \(\mathrm{Z=8}\)
- Site 3: \(\mathrm{W=33}\), \(\mathrm{Z=11}\)
- Site 5: \(\mathrm{W=3}\), \(\mathrm{Z=37}\)
- (See other sites for confirmation. X is nearly constant. Y is positively correlated with W.)
- Calculations Estimations:
Z is low when W is high (Sites 1 and 3), and Z is high when W is low (Site 5). This is a consistent negative pattern.
- Comparison to Answer Choices:
X: no correlation. Y: positive correlation. Z: clear negative correlation. Therefore, Z is the correct choice for strongest negative correlation.
FINAL ANSWER Blank 2: Z
Summary
X is nearly constant, so it is not correlated with W. Y rises and falls with W at most sites, indicating a positive correlation. Z shows the opposite trend and is highest where W is lowest, indicating a strong negative correlation. Thus, the correct answers are Y (positive correlation) and Z (negative correlation).
Question Independence Analysis
The two blanks are independent because one requires identifying the species most in sync with W and the other requires finding the species most out of sync. Answering one does not logically require knowing the other, as each relies on a separate pattern of relationship with W.