Loading...
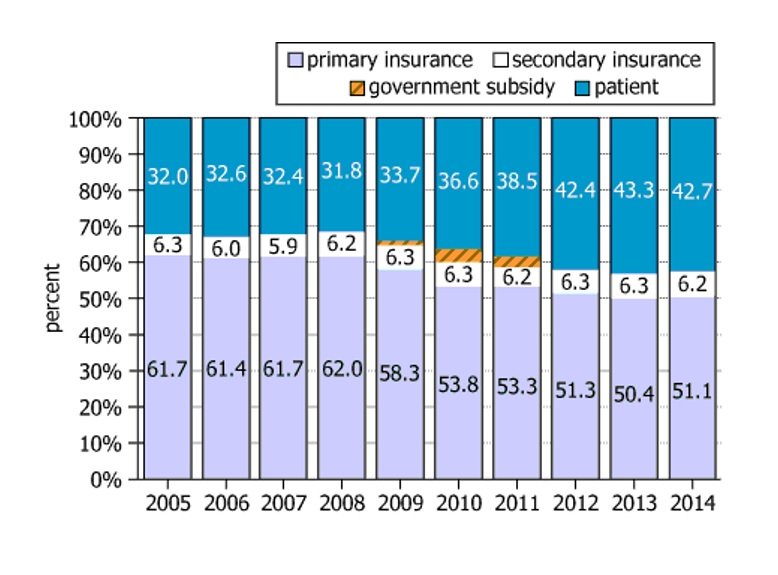
The graph shows the distribution of funding sources for medical expenses incurred at a certain hospital in Country C for the years 2005-2014. For example, in 2005, 61.7% of medical expenses incurred at this hospital were paid by the patient's primary insurance, 6.3% by the patient's secondary insurance, and 32.0% by the patient. In the years 2009, 2010, and 2011, the government of Country C provided a subsidy that paid a small percent of the medical expenses.
| Text Component | Content/Meaning |
|---|---|
| Context | Distribution of funding sources for medical expenses at a hospital in Country C (2005-2014) |
| Payment sources identified | Primary insurance, secondary insurance, patient, (and government subsidy in 2009-2011) |
| Example breakdown (2005) | \(61.7\%\) primary insurance, \(6.3\%\) secondary insurance, \(32.0\%\) patient |
| Special case | Government subsidized a small percent in 2009, 2010, 2011 |
| Data type | Percent paid per source per year, all sum to 100% |
| Chart Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Chart type | 100% stacked bar chart (years 2005-2014 on X-axis, percent of expense on Y-axis) |
| Categories shown | Primary insurance, secondary insurance, patient, government subsidy |
| Trend primary ins. | Decreases from \(61.7\%\) (2005) to \(50.4\%\) (2013) |
| Trend patient | Increases from \(32.0\%\) (2005) to \(43.3\%\) (2013) |
| Trend secondary ins. | Remains stable around 6-6.3% throughout |
| Gov't subsidy | Present only in 2009, 2010, 2011 (small percent) |
Over the ten-year period, the portion of medical expenses paid by patients rose steadily, while coverage from primary insurance declined. Secondary insurance remained a small, constant contributor. The government only briefly subsidized expenses (2009-2011), indicating a short-term intervention. By 2013, patients bore a much higher share of costs than in 2005.
The ratio of the percent paid by the patient to the percent paid by the patient's primary insurance was greatest in the year [BLANK 1]
The ratio of the percent paid by the patient to the percent paid by the patient's primary insurance was least in the year [BLANK 2]
Over the years, the share of medical expenses paid by patients increased while the share paid by primary insurance decreased. Thus, the patient-to-primary insurance ratio was the greatest in 2013 (about \(0.86\)) and the least in 2008 (about \(0.51\)).
These blanks are independent: Blank 1 asks for the year with the highest patient-to-insurance ratio from one group of years, while Blank 2 asks for the lowest from a separate group. Finding one does not determine the other.