Loading...
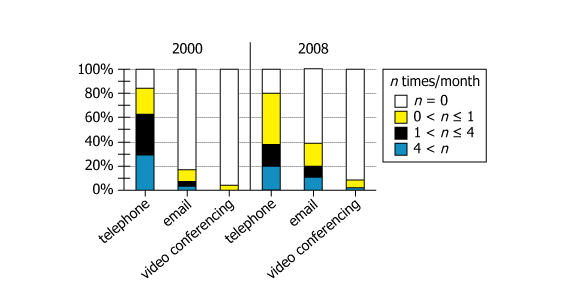
The graph shows data for physicians who, in 2000 and 2008, were surveyed about the average number of times per month they used each of 3 methods (telephone, email, and video conferencing) to communicate with their patients. The bars represent the percentage of the respondents who reported using the indicated method the indicated number of times per month.
Select from each drop-down menu the option that completes the statement so that it most accurately reflects the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Survey subjects | Physicians in 2000 and 2008 | Doctors surveyed in two years |
| Methods surveyed | Telephone, email, and video conferencing | Three ways doctors communicate with patients |
| Measurement | Average number of times per month for each method | How often each communication method was used monthly |
| Data presented as | Bars represent % of respondents for each method & frequency range | For each method/frequency, percent of doctors who use it that much |
| Frequency categories | \(\mathrm{n=0}\); \(\mathrm{0\lt n≤1}\); \(\mathrm{1\lt n≤4}\); \(\mathrm{4\lt n}\) | Four bins: never, rare, moderate, frequent communications |
| Purpose | Communicate with patients | All communication methods are for doctor-patient contact |
| Chart Component | What's Shown | What This Indicates |
|---|---|---|
| Layout | Side-by-side bars for 2000 and 2008, for each method | Allows direct year-to-year comparison for each method |
| Frequency distribution | Stacked colored bar segments (four frequency bins per method per year) | Reveals spread of doctor usage—most never or rarely used email or video |
| Telephone (2000 vs 2008) | Frequent (\(\mathrm{4\lt n}\)) users decreased (\(\mathrm{25\%→20\%}\)); rare users (\(\mathrm{0\lt n≤1}\)) increased (\(\mathrm{10\%→31\%}\)) | More doctors used phone infrequently in 2008; fewer used it very often |
| Email (2000 vs 2008) | Non-users decreased (\(\mathrm{72\%→60\%}\)); moderate/frequent users increased (\(\mathrm{1≤n≤4: 18\%→25\%; 4\lt n: 2\%→10\%}\)) | Email use became more common, but most still didn't use it monthly |
| Video conferencing (2000/08) | Non-users: \(\mathrm{96\%→90\%}\); minor rise in any use (all below \(\mathrm{1\lt n≤4}\) or \(\mathrm{4\lt n}\) in both years) | Video use remained rare, but more doctors tried it by 2008 |
It must be the case that the median number of times per month respondents reported having communicated with patients by [BLANK 1] in the 2008 survey was less than that in the 2000 survey.
It must be the case that the percentage of respondents who reported having communicated with patients by both [BLANK 2] was as great or greater in the 2008 survey as it was in the 2000 survey.
For Blank 1, only telephone showed a decrease in median frequency category between 2000 and 2008. For Blank 2, only the combination of telephone and email meets the requirement that their minimum joint user percentage in 2008 was at least as great as the maximum in 2000.
The two blanks are independent. Blank 1 asks about the change in median usage for an individual communication method, while Blank 2 focuses on the joint use of pairs of methods. Their solutions do not rely on one another.