Loading...
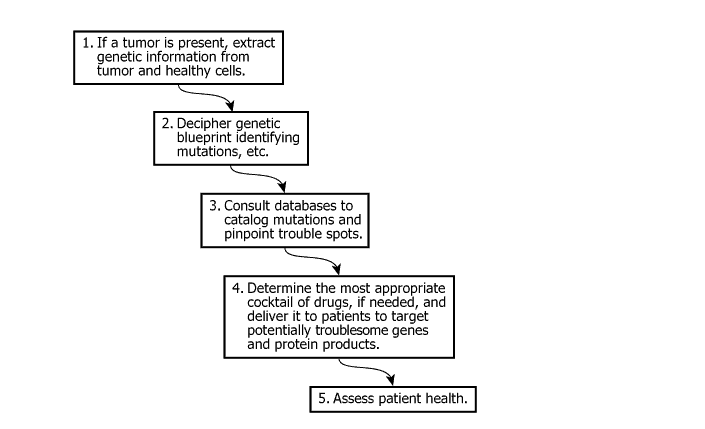
The flowchart indicates the steps in the process of comprehensive genetic tumor testing that doctors hope will provide cancer sufferers with personalized treatment. Arrows indicate the next step needed in the process.
On the basis of the information provided, select from each drop-down menu the option that creates the most accurate statement.
| Text Component | Content | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Process Description | The flowchart indicates the steps in the process of comprehensive genetic tumor testing | Explains the chart shows steps in genetic tumor testing |
| Purpose | Doctors hope will provide cancer sufferers with personalized treatment | Aim is personalized cancer treatment |
| Navigational Instruction | Arrows indicate the next step needed in the process | Arrows show sequence/order of steps |
| Chart Element | Description | Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Vertical flowchart with 5 steps, each in a box, connected by downward arrows | Illustrates a sequential medical testing process |
| Step 1 | If tumor is present, extract genetic information from tumor and healthy cells | Begin by sampling genetic material from patient |
| Step 2 | Decipher genetic blueprint identifying mutations, etc. | Analyze for gene mutations |
| Step 3 | Consult databases to catalog mutations and pinpoint trouble spots | Compare findings with known mutations |
| Step 4 | Determine the most appropriate cocktail of drugs, if needed, and deliver it... | Use genetic info to select and administer treatment |
| Step 5 | Assess patient health | Monitor patient response to treatment |
| Arrow Structure | All arrows are directed downward, connecting steps 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5, no feedback arrows | Process is strictly linear, no repeats, no feedback |
The dataset represents a strictly linear step-by-step workflow for genetic tumor testing and treatment selection, with no feedback loops. Each step (from genetic sampling to patient health assessment) is distinct and sequential, culminating with patient monitoring as the terminal step. There is no visual or textual indication of reassessment or iterative feedback to earlier steps, which highlights a potential limitation for dynamic, adaptive treatment approaches.
An arrow extending from Box 5 to Box [BLANK] would address the fact that tumor cells can mutate over time.
An arrow extending from Box 5 to Box [BLANK] would address the fact that knowledge about the effects of particular drugs on particular genetic mutations and their protein products is constantly changing.
A feedback arrow from Box 5 to Box 1 allows the process to capture new tumor mutations by repeating genetic extraction when patient health changes. A feedback arrow from Box 5 to Box 4 allows the process to adapt to new drug knowledge by updating treatment decisions for the patient without needing to re-analyze existing data.
The two questions are related by focusing on feedback from patient assessment (Box 5) but address different causes for repetition: biological changes (mutation) versus knowledge changes (drug research). Each blank can be answered independently by identifying which earlier step is most directly relevant to the stated issue.