Loading...
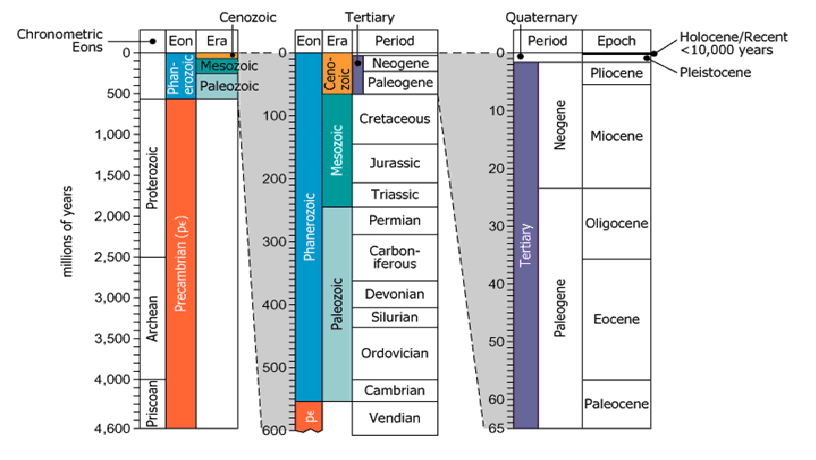
The diagram shows, in three column groupings, various divisions of Earth's geological history since its formation approximately 4,600 million years ago. In the leftmost column grouping, the Precambrian eon is subdivided into chronometric eons shown on the far left; but otherwise, in the rest of the graphic, each subsequent column to the right shows the subdivisions of the timeframes to its left. Each of the rightmost two column groupings is a magnification—with additional information—of a portion of the grouping directly to its left.
Fill each blank using the drop-down menu to create the most accurate statement on the basis of the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Overall diagram structure | The diagram shows, in three column groupings, various divisions of Earth's geological history | The diagram uses three columns to display different hierarchical breakdowns of Earth's timeline |
| Time span covered | Since its formation approximately 4,600 million years ago | The diagram covers all of Earth's 4.6 billion-year history |
| Precambrian structure | The Precambrian eon is subdivided into chronometric eons shown on the far left | The oldest time unit, Precambrian, is further divided in the first column |
| Column relationship | Each subsequent column to the right shows the subdivisions of the timeframes to its left | Each column zooms in by breaking down previous timeframes into more granular units |
| Magnification concept | Each of the rightmost two column groupings is a magnification—with additional information—of a portion of the grouping directly to its left | The two right columns are focused, more detailed views of slices from prior columns |
| Chart Component | What's Shown | What This Tells Us |
|---|---|---|
| Chart type | Three adjacent vertical stacked bars/timelines | Shows hierarchical structure of Earth's time visually |
| Vertical axis | Time in millions of years (Ma); 0 at top, 4600 at bottom | Follows convention; aligns present at top, origin at bottom |
| Color coding | Color blocks represent different eons, eras, periods, etc. | Hierarchy is made visually distinct for clarity |
| Leftmost column | Whole 4.6 billion-year history; big units like eons | Full context for all time; shows broadest divisions |
| Middle and right columns | Progressive magnification; eras, then periods/epochs | More recent time gets more detailed breakdowns |
| Phanerozoic boundary | Phanerozoic starts 541 Ma, matching new eon, era, period | This marks a triple boundary in geological time |
| Cenozoic/Neogene/Miocene | Cenozoic (66-0 Ma), Neogene (23–2.6 Ma), Miocene within Neogene | Cenozoic is 66m years; Neogene is ~31% of Cenozoic; Miocene is a major part of Neogene |
The Miocene epoch spans closest to _______ of the era of which it is a part.
According to the diagram the beginning of the _______ marks the onset of a new eon, era, and period in geological history.
By analyzing durations and boundaries in the geological time chart, we find the Miocene makes up roughly 25% of the Cenozoic era, and that the Cambrian period marks the simultaneous start of a new eon, era, and period in geological history.
These questions are independent: the first concerns proportional duration within an era, the second concerns boundary alignment for major time divisions. No information from one is needed to answer the other.