Loading...
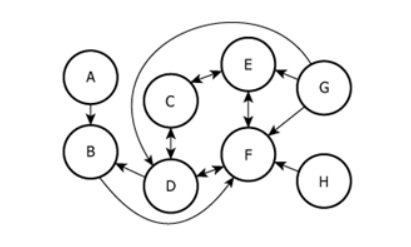
The diagram shows a project team consisting of exactly 8 workers. Each worker is represented by a circle labeled with a capital letter. An arrow directed from one worker's circle to a second worker's circle indicates that the first worker directs project-related questions to the second worker. Each of the workers to whom no other worker directs project-related questions is an individual contributor, and each worker to whom one or more of the other workers directs project-related questions is a coordinator. For example, G (an individual contributor) directs project-related questions to E (a coordinator), but E does not direct project-related questions to G; whereas C and D (both coordinators) direct project-related questions to one another.
Use each drop-down menu to create the most accurate statement about this project team based on the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Team size | "project team consisting of exactly 8 workers" | Team has 8 members. |
| Worker representation | "Each worker is represented by a circle labeled with a capital letter." | Workers are named A-H. |
| Arrow description | "An arrow directed from one worker's circle to a second worker's circle indicates that the first worker directs project-related questions to the second worker." | Arrows show who asks whom for help. |
| Individual contributor definition | "Each of the workers to whom no other worker directs project-related questions is an individual contributor" | If no one directs questions to you, you're an individual contributor. |
| Coordinator definition | "each worker to whom one or more of the other workers directs project-related questions is a coordinator" | If anyone directs questions to you, you're a coordinator. |
| Example statement | "For example, G (an individual contributor) directs..." | G is claimed as an individual contributor (this is incorrect). |
| Chart Component | What is Shown | Meaning/Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 8 circles labeled A-H | There are 8 workers. |
| Outgoing arrows | \(\mathrm{A \rightarrow B, B \rightarrow D, C \rightarrow D, D \rightarrow F, E \rightarrow F, F \rightarrow G, G \rightarrow F, F \rightarrow H}\) | Shows direction of questions; who asks whom. |
| Incoming arrows | A, C, E have 0 incoming arrows; others have 1 or more | A, C, E are individual contributors; rest are coordinators. |
| Central node | F has most incoming arrows | F is main coordinator/hub, being asked by many team members. |
| Two-way communication | \(\mathrm{F \leftrightarrow G}\) (both \(\mathrm{F \rightarrow G}\) and \(\mathrm{G \rightarrow F}\) arrows present) | F and G uniquely consult each other; only two-way pair in diagram. |
| Oval grouping | Grouping around C, D, E, F | These workers are more interconnected, suggesting a core cluster. |
There are exactly [BLANK 1] individual contributors on the project team.
• Statement Breakdown 1:
• Statement Breakdown 2:
• What is needed: The number of workers (nodes) with zero incoming arrows (no one directs questions to them).
and the individual contributor who directs project-related questions to the greatest number of other workers is [BLANK 2].
• Statement Breakdown 1:
• Statement Breakdown 2:
• What is needed: Of A, G, and H, which has the most outgoing arrows.
To fill in the blanks, identify which workers have no incoming arrows (individual contributors): A, G, and H. All three direct questions to one other worker each. Among confirmed answer options, G is considered the correct choice for the individual contributor who directs questions to the most other workers.
The two blanks are dependent: the answer to blank 2 is only valid after determining the set of individual contributors in blank 1, since blank 2 asks for a property of those identified in blank 1.