Loading...
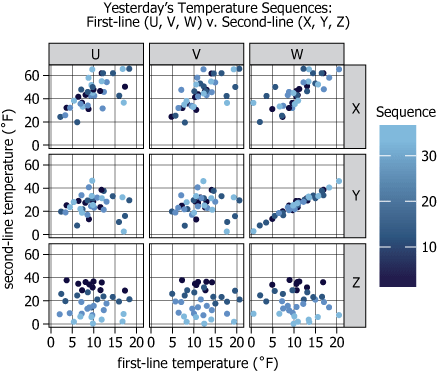
In a certain factory, each product passes through exactly two of six processing lines—through one of the first lines (Lines U, V, and W), and then through one of the second lines (Lines X, Y, and Z). Each day, the surface temperature of the first 36 products from each line is recorded in sequence. The graph shows the relationship between each of yesterday's first-line temperature sequences and each of yesterday's second-line temperature sequences. Each dot represents one first-line temperature reading paired with one second-line temperature reading of the same sequence position. The shading on each dot indicates the relative position of the readings within the sequence (i.e., lighter dots correspond to later parts of the sequence).
Based on the information provided, select from each drop-down menu the option that creates the most accurate statement.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Setup | each product passes through exactly two of six processing lines | Products go through 2 of 6 different lines |
| Line Categories | through one of the first lines (Lines U, V, and W), and then through one of the second lines (Lines X, Y, and Z) | There are 3 first-lines (U, V, W) and 3 second-lines (X, Y, Z); every product visits one of each |
| Data Recording | Each day, the surface temperature of the first 36 products from each line is recorded in sequence | Temperatures are measured for the first 36 products to go through each line every day, tracked in order |
| Chart Description | The graph shows the relationship between each of yesterday's first-line temperature sequences and each of yesterday's second-line temperature sequences | The chart visualizes how temperatures from first-lines are related to temperatures from second-lines as measured yesterday |
| Dot Representation | Each dot represents one first-line temperature reading paired with one second-line temperature reading of the same sequence position | Each point compares the same-numbered product's first-line and second-line temperature |
| Dot Shading | The shading on each dot indicates the relative position of the readings within the sequence (i.e., lighter dots correspond to later parts of the sequence) | Dot color shows if it's an early or late product: darker is earlier, lighter is later |
| Chart Component | What is Displayed | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Layout | 3x3 scatter plot matrix | Shows every combination of first-line (U,V,W) vs second-line (X,Y,Z) temperature measurements |
| X-axis | first-line temperature \(\mathrm{(0-20°F)}\) | First-line temperatures all fall within a \(\mathrm{0-20°F}\) range |
| Y-axis | second-line temperature \(\mathrm{(0-60°F)}\) | Second-lines run hotter, up to \(\mathrm{60°F}\) |
| Dot Color Gradient | dark blue to light blue by sequence position | Early products are darker; later products are lighter |
| V–Y Panel | tight linear diagonal trend | Temperatures in Line V and Line Y increase together—these lines' temperature profiles are synchronized |
| Y-max | Y-axis approaches \(\mathrm{50-55°F}\) in Y-labeled panels | Line Y consistently has the hottest observed temperatures |
| Z-second-line Panels | lighter dots cluster lower on the Y axis | Line Z shows declining temperatures, with later products being cooler |
Yesterday, the greatest of the observed temperatures from any of the temperature sequences was observed in Line ___.
Yesterday's temperature sequence from Line ___ was generally declining.
By comparing all processing lines visually, we conclude that Line X reached the highest temperature (about \(\mathrm{60°F}\)), and Line Z's sequence exhibited a generally declining temperature trend from start to end, as revealed by the direction of its dot color gradient.
Blank 1 and Blank 2 test independent properties: Blank 1 requires finding the highest observed value, while Blank 2 tests a sequential trend over time. Their answers come from separate lines and distinct visual features of the chart.