Loading...
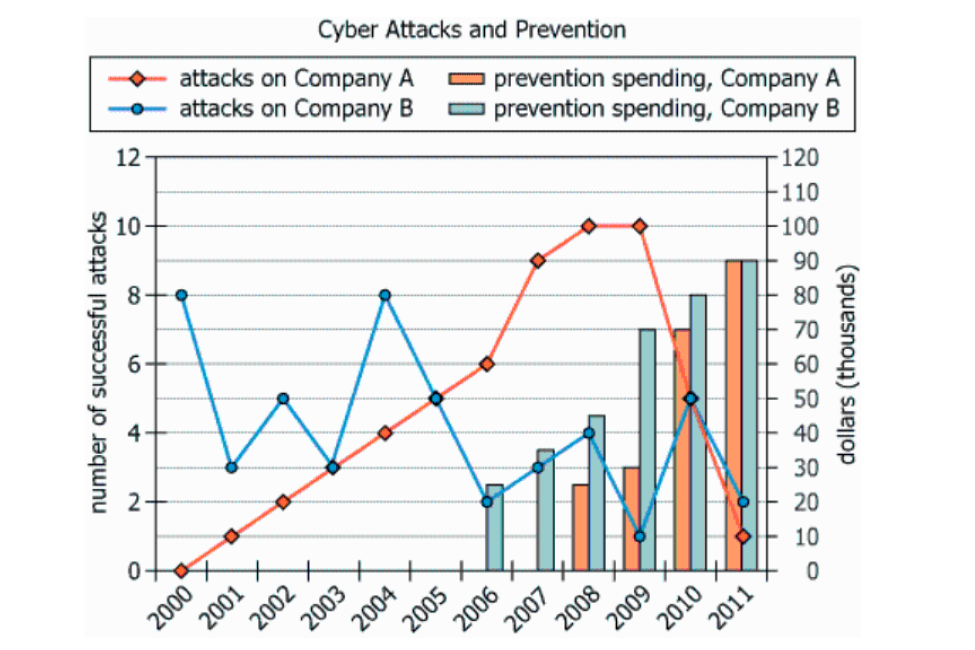
For the years 2000 to 2011, the graph shows for the number of successful cyber attacks that year on two companies, as well as the amount of money (in thousands of dollars) each company spent that year in prevention of cyber attacks. Neither company had experienced successful cyber attacks before the year 2000.
Use the drop-down menus to form the most accurate statements based on the given information.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | For the years 2000 to 2011 | Data covers 12 consecutive years starting at 2000 |
| Primary Data Shown | The number of successful cyber attacks that year on two companies | Each year shows how many attacks each company experienced |
| Secondary Data Shown | The amount of money (in thousands of dollars) each company spent that year in prevention | Reveals yearly cybersecurity investment for both companies in $1,000 units |
| Historical Context | Neither company had experienced successful cyber attacks before the year 2000 | Baseline: attacks begin only in 2000, prior years are zero |
| Chart Element | Description | Implication or Pattern Identified |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Combined line and bar chart | Allows simultaneous view of incidents (lines) and spending (bars) |
| X-axis | Years 2000-2011 | Annual tracking across 12 years |
| Left Y-axis | Number of attacks (range approx. 0-12) | Annual attacks ranged from 0 to a high near 10 |
| Right Y-axis | Prevention spending ($ thousands, up to $90,000 per company) | Spending gradually increased, peaking in 2011 |
| Attack Series | Red diamonds: Company A attacks; Blue circles: Company B attacks | Company A's attacks peak mid-series, fall sharply later; Company B fluctuates, also falls by end |
| Spending Series | Orange bars: Company A spending (starts 2008); Blue bars: Company B spending (starts 2006) | Company B starts investing earlier; both reach $90k in 2011 |
| General Trends | Attacks rise, then drop as prevention spending increases (especially post-2008) | Suggests increased spending correlates with decreased attacks |
From 2000 to 2011, the number of successful cyber attacks that Company A experienced was [BLANK] the number of successful cyber attacks that Company B experienced.
The only year where increased spending coincided with a decrease in successful cyber attacks (compared to the previous year) for both companies was [BLANK].
Company A experienced a greater total number of successful cyber attacks than Company B from 2000 to 2011. The unique year when both companies had increased prevention spending and fewer attacks was 2011.
The two questions are independent. The first concerns overall totals over the whole period, while the second is about a single year with specific conditions; solving one does not require knowledge of the other.