Loading...
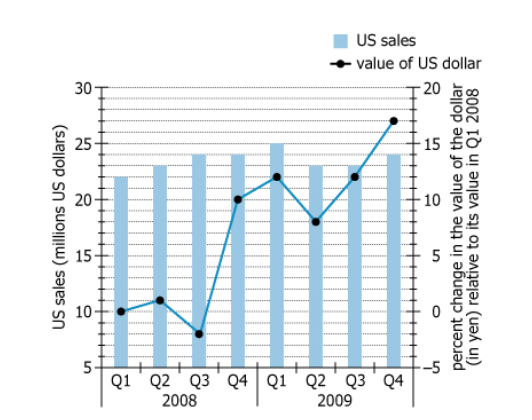
For each of the 8 quarters of 2008-2009, the graph shows a Japanese electronics firm's total US sales (rounded to the nearest 1 million US dollars), and the change in the average value of US dollar in Japanese yen, where the change is expressed as a percentage of the dollar's value in the first quarter of 2008 (Q1 2008), to the nearest 1 percent. For any given quarter, this data may be used to convert total US sales to their Q1 2008 yen equivalent: a value directly proportional to that quarter's total US sales in Q1 2008 yen.
On the basis of the information provided, select from each of the drop-down menus the option that created the most accurate statement.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | Japanese electronics firm | Japanese company selling electronics |
| Data series | Total US sales and change in average value of US dollar in Japanese yen | Amount sold in US dollars and percentage change in dollar-yen exchange rate |
| Time period | 8 quarters of 2008-2009 | Data covers two years, divided by quarter |
| US sales units | Rounded to the nearest 1 million US dollars | Sales numbers are approximate and easy to compare |
| Dollar value change | Expressed as percentage of the dollar's value in Q1 2008 | All currency values compare back to early 2008 |
| Conversion ability | Use data to convert total US sales to their Q1 2008 yen equivalent | Can adjust sales figures by currency changes for consistent comparison |
| Chart Component | What It Shows | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Combo of bar and line charts | Displays two series: sales and exchange rate changes |
| Bar chart (blue bars) | Total US sales (in millions) by quarter | Range is 22–25 million; relatively stable across all quarters |
| Line chart (black with dots) | % change in average dollar value vs. Q1 2008 | Ranges from \(-2\%\) (lowest) to \(+17\%\) (highest) |
| X-axis | Quarters (Q1 2008 to Q4 2009) | Eight quarters in order |
| Left y-axis | US sales scale: 0–30 million | Used for blue bars |
| Right y-axis | % change scale: \(-5\%\) to \(+20\%\) | Used for dollar value change; most values are positive after Q2 2008 |
| General trend | Dollar strengthens 2008–2009; sales stay steady | Converts to higher yen-equivalent in 2009, especially late 2009 |
During 2008–2009, the Japanese electronics firm's US sales remained steady, but the US dollar became much stronger against the yen—especially in 2009, peaking at a \(17\%\) increase in Q4 2009 versus the Q1 2008 baseline. Because yen-equivalent sales are calculated as US sales multiplied by (1 + percentage change), quarters with a strong dollar (like Q4 2009) see their sales worth much more in yen when measured by Q1 2008 rates. In contrast, Q3 2008 had the weakest dollar (\(-2\%\)), so yen-equivalent sales are lowest there, despite actual US sales staying fairly constant.
Q1 2008 yen-equivalent sales were highest in [BLANK] of 2009.
Q1 2008 yen-equivalent sales for Q4 2009 were [BLANK] Q1 2008 yen-equivalent sales for Q4 2008.
Q1 2008 yen-equivalent sales were highest in Q4 2009, just surpassing Q1 2009 because the strong percentage appreciation of the dollar against the yen outweighed Q1's slightly higher US sales. Comparing Q4 of 2009 and 2008, yen-equivalent sales were greater in 2009 due to a higher percentage increase, despite identical US dollar sales in both quarters.
While both questions require the same formula and chart interpretation, each can be answered independently using basic calculations and data extraction. Understanding one does not directly affect solving the other.