Loading...
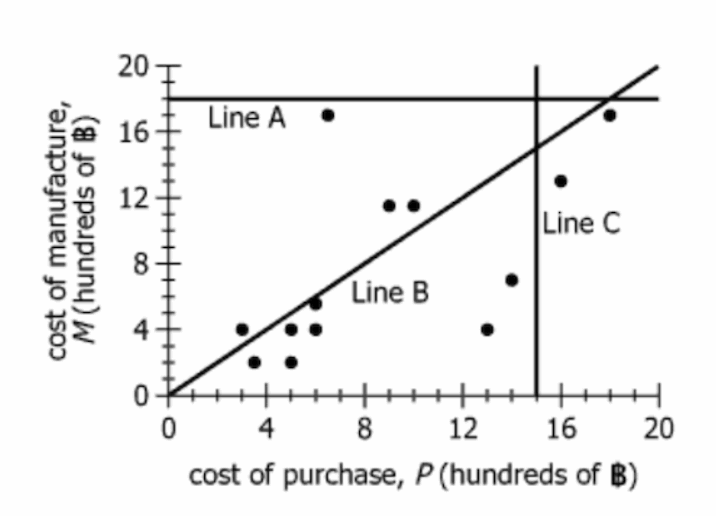
For a manufacturing company in Thailand, the graph displays data on the cost of purchase from an outside supplier (P) versus the cost of in-house manufacture (M), in hundreds of Thai baht (B), for 13 different industrial parts. For each of the 13 parts, if \(\mathrm{M} < \mathrm{P}\), the company will manufacture that part in-house. There is a fixed value, k, such that for any of the 13 parts, if \(\mathrm{k} \geq \mathrm{M} \geq \mathrm{P}\), the company will purchase the part from an outside supplier; if \(\mathrm{P} \geq \mathrm{k}\), the company will manufacture the part in-house, even if \(\mathrm{M} \geq \mathrm{P}\). The graph also displays 3 lines, one of which represents the maximum amount the company will pay to purchase a part from an outside supplier.
Use the drop-down menus to create the most accurate statements based on the information provided.
| Text Component | Content |
|---|---|
| Company context | Manufacturing company in Thailand |
| Data measured | Cost of purchase from outside supplier (P) vs. cost of in-house manufacture (M) |
| Measurement units | Hundreds of Thai baht |
| Number of parts | 13 different industrial parts |
| Primary decision rule | If \(\mathrm{M \lt P}\), manufacture in-house |
| Special threshold (k) | If \(\mathrm{k ≥ M ≥ P}\), purchase from supplier; if \(\mathrm{P ≥ k}\), manufacture in-house, even if \(\mathrm{M ≥ P}\) |
| Graph details | 3 lines shown (one representing maximum purchase cost from outside supplier); data points represent 13 parts |
| Chart Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chart type | Scatterplot with 13 data points (each point: a part, P on x-axis, M on y-axis) |
| X-axis | Cost of purchase (P), in units of 100 Thai baht |
| Y-axis | Cost of in-house manufacture (M), in units of 100 Thai baht |
| Reference lines | Diagonal (\(\mathrm{M = P}\)); vertical line at \(\mathrm{P = k}\) (maximum the company will pay); possibly horizontal at \(\mathrm{M = k}\) |
| Point locations | Many points above the diagonal (\(\mathrm{M \gt P}\)); a few below (\(\mathrm{M \lt P}\)) |
| Value spread | P and M values roughly between 0 and 20 (i.e., 0—2000 Thai baht) |
The graph displays data for _____ industrial parts for which the cost of in-house manufacture exceeds the cost of purchase from an outside supplier.
Statement Breakdown 1:
Statement Breakdown 2:
What is needed: The number of points (industrial parts) above Line B, i.e., with \(\mathrm{M \gt P}\).
For industrial parts for which the cost of in-house manufacture exceeds the cost of purchase from an outside supplier, the maximum cost of purchase is _____.
Statement Breakdown 1:
Statement Breakdown 2:
What is needed: The highest purchase cost (P) among the 4 parts above Line B.
To answer the first blank, we counted points above Line B, giving 4. For blank two, we found the maximum purchase cost among these, which is 1000 baht. Both answers require careful reading of the graph, and blank 2 depends on the identification made in blank 1.
The questions are dependent: to answer the second, you need to correctly identify the subset of parts where \(\mathrm{M \gt P}\), which is the answer to the first question.