Loading...
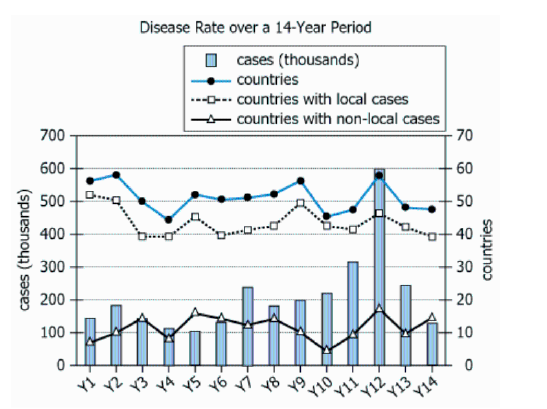
An international health organization collected global data regarding a certain disease for each of 14 consecutive years (Y1 – Y14). The graph shows the annual numbers of cases, countries, countries with local cases (i.e., cases for which the infection was contracted within the country), and countries with non-local cases (i.e., cases for which the infection was contracted outside of the country).
From each drop-down menu, select the option that creates the most accurate statement according to the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collector | An international health organization | Reputable, global data source |
| Subject | Collected global data regarding a certain disease | Study focuses on one disease, not named |
| Time Frame | Each of 14 consecutive years \(\mathrm{(Y1–Y14)}\) | Annual data, labeled Y1 to Y14, over 14 years |
| Annual Cases | Annual numbers of cases | Total number of disease cases reported each year |
| Countries | Annual numbers of countries | How many countries reported disease occurrence annually |
| Local Cases | Countries with local cases (infection contracted within the country) | Countries with in-country transmission |
| Non-local Cases | Countries with non-local cases (infection contracted outside the country) | Countries with travel/imported cases |
| Chart Element | What it Shows | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Chart Type | Combination bar and line chart, dual Y-axes | Multiple data types visualized; direct time series comparison |
| X-Axis | Years \(\mathrm{Y1−Y14}\) | 14-year timeline, aligns with text description |
| Left Y-Axis | \(\mathrm{0–700}\) (in thousands, for cases) | Disease case counts (e.g., up to 600,000) |
| Right Y-Axis | \(\mathrm{0–70}\) (for countries) | Number of affected countries (max observed ≈ 59) |
| Blue Bars | Case numbers per year | Visualizes fluctuations, particularly a major spike in Y12 |
| Solid Line | Total countries affected each year | Shows stable range (about 45–59 countries/year) |
| Dashed Line | Countries with local cases per year | Usually just below total countries; most cases are local |
| Y12 Spike | Large increase in blue bar | Dramatic uptick in cases without rise in affected countries |
The percent increase in the number of cases of the disease from Y9 to Y12 was, to the nearest 10%, ______.
What is needed: The percentage increase in disease cases from Y9 to Y12, rounded to the nearest 10%.
The average (arithmetic mean) of the numbers of countries with local cases from Y1 to Y5 was, to the nearest 5 countries, ______.
What is needed: The mean (rounded to the nearest 5) of local-cases countries from Y1 to Y5.
For blank 1, a direct application of the percent increase formula shows cases tripled from Y9 to Y12, resulting in a 200% increase. For blank 2, averaging the first five dashed line values and rounding gives 45 countries. Both use distinct data and math.
The questions are independent. Blank 1 uses bar graph values (cases) and years 9 and 12, while blank 2 uses dashed line values (countries) and years 1 through 5. Solving one does not assist with the other.