Loading...
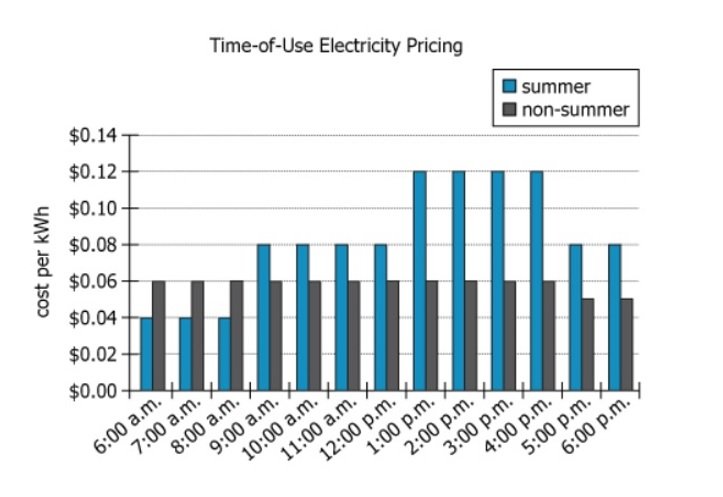
A utility company sells electricity to its customers by units of energy called kilowatt hours (kWh). In order to encourage its customers to use less electricity during periods of peak electrical demand in the summer, the company charges its customers a higher amount per kWh for electricity during peak usage times. The graph shows the amount, in USD per kWh, that the company charges its customers for electricity during both the summer and non-summer months, from the hours of 6:00 a.m. until 6:00 p.m. The utility company charges the same price per kWh in the summer and non-summer months for all hours of the day not depicted in the graph.
Select from each drop-down menu the option that creates the most accurate statement based on the information provided.
| Text Element | Direct Text | Summary Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity unit | '...sells electricity to its customers by units of energy called kilowatt hours (kWh).' | Electricity is sold in kWh units. |
| Time-of-use pricing | '...the company charges its customers a higher amount per kWh for electricity during peak usage times.' | Customers pay more per kWh during certain (peak) hours in summer. |
| Graph coverage | 'The graph shows the amount, in USD per kWh, ... during both the summer and non-summer months, from ... 6:00 a.m. until 6:00 p.m.' | Graph displays detailed hourly prices for summer vs non-summer, 6am–6pm. |
| Pricing outside range | '...the utility company charges the same price per kWh ... for all hours of the day not depicted in the graph.' | For hours not shown (outside 6am–6pm), price is the same in both seasons. |
| Aspect | What the Chart Shows | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Chart format | Grouped bar chart: summer vs non-summer price for each hour from 6am to around 7pm | Enables hour-by-hour seasonal comparison |
| Summer pricing | 3 tiers: \(\$0.04/\mathrm{kWh}\) (6–8:59am), \(\$0.08/\mathrm{kWh}\) (9am–12:59pm, 5–6:59pm), \(\$0.12/\mathrm{kWh}\) (1–4:59pm) | Summer prices fluctuate—cheapest early, highest mid-afternoon |
| Non-summer pricing | Mostly \(\$0.06/\mathrm{kWh}\) (6am–4:59pm), \(\$0.05/\mathrm{kWh}\) (5–6:59pm) | Non-summer prices are stable and lower overall |
| Summer lower than non-summer | Only from 6am–8:59am: summer (\(\$0.04\)) < non-summer (\(\$0.06\)) | Early morning is the only time summer is cheaper |
| Peak summer rates | \(\$0.12/\mathrm{kWh}\) (1–4:59pm): double the non-summer price | Strongest incentive to reduce use during summer afternoons |
Summer electricity is cheaper than non-summer only from 6:00–8:59 a.m. (\(\$0.04\) vs \(\$0.06\) per kWh). The utility implements a clear three-tier summer price system (\(\$0.04/\$0.08/\$0.12\)) to discourage peak afternoon use, in contrast to relatively flat pricing in non-summer months. This incentivizes customers to shift their summer electricity consumption to early morning, reducing stress on the power grid during peak hours.
During the times depicted in the graph, the utility company charges customers more per kWh in the summer months than it does in the non-summer months, except during the hours from [BLANK 1],
What is needed: The time period during which summer rates are lower than non-summer rates.
when the utility company charges [BLANK 2] less per kWh than it charges during the non-summer months.
What is needed: The exact numerical difference in rates between non-summer and summer during 6:00 a.m. through 8:59 a.m.
Generally, summer electricity rates are higher than non-summer rates. The only exception in the chart is from 6:00 a.m. through 08:59 a.m., where the summer rate is actually \(\$0.02\) per kWh lower than the non-summer rate. Recognizing this exception requires careful comparison across the time periods shown on the graph.
Blank 1 and Blank 2 are dependent: once you determine the time period for Blank 1, you must use that specific period to calculate the price difference for Blank 2.