Loading...
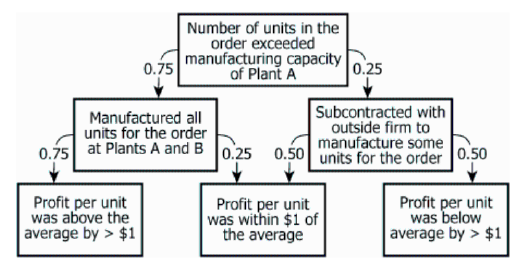
A particular manufacturing company has exactly two manufacturing plants–Plants A and B. A consultant, using data about the company's past performance and a particular model, calculated the probability of various outcomes when the company has promised to manufacture an order consisting of a greater number of units than could be produced only at the main plant, Plant A. Those probabilities are shown in the chart.
Select from each drop-down menu the opfon that creates the statement that most accurately reflects the information given.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Company Structure | has exactly two manufacturing plants–Plants A and B | The company has only 2 manufacturing facilities |
| Main Plant | the main plant, Plant A | Plant A is the primary plant; Plant B is auxiliary |
| Order Context | an order consisting of a greater number of units than could be produced only at Plant A | Analysis is for large orders exceeding Plant A's capacity |
| Probability Calculation Basis | using data about the company's past performance and a particular model | Past data and modeling are used for probability estimates |
| Probability Display | calculated the probability of various outcomes ... shown in the chart | The chart summarizes all relevant probabilities |
| Chart Component | What's Shown | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Root Node | Order exceeds Plant A's capacity | All scenarios are for large orders |
| First Branch | 75% In-house (A+B), 25% Subcontract | Company mostly prefers in-house production |
| In-house Outcomes | 75% profit >$1 above average, 25% within $1 of avg. | In-house yields mainly high profits, moderate profit also possible |
| Subcontract Outcomes | 50% profit >$1 above, 50% profit >$1 below average | Subcontracting leads to only extreme profit outcomes |
The chart indicates that, for an order selected at random from those consisting of more units than could be produced by Plant A, the probability that the company's profit per unit on that order was within $1 of the average is equal to the sum of [BLANK 1] and...
...and [BLANK 2]
To find the required probability, add the probabilities of both manufacturing and subcontracting branches leading to 'profit within $1 of average'. The total is \(0.1875 + 0.125 = 0.3125\).
BLANK 1 and BLANK 2 correspond to distinct branches (manufacturing and subcontracting, respectively), but both are required to find the total probability as specified by the question. Thus, they are related and dependent in the context of solving the problem.