Loading...
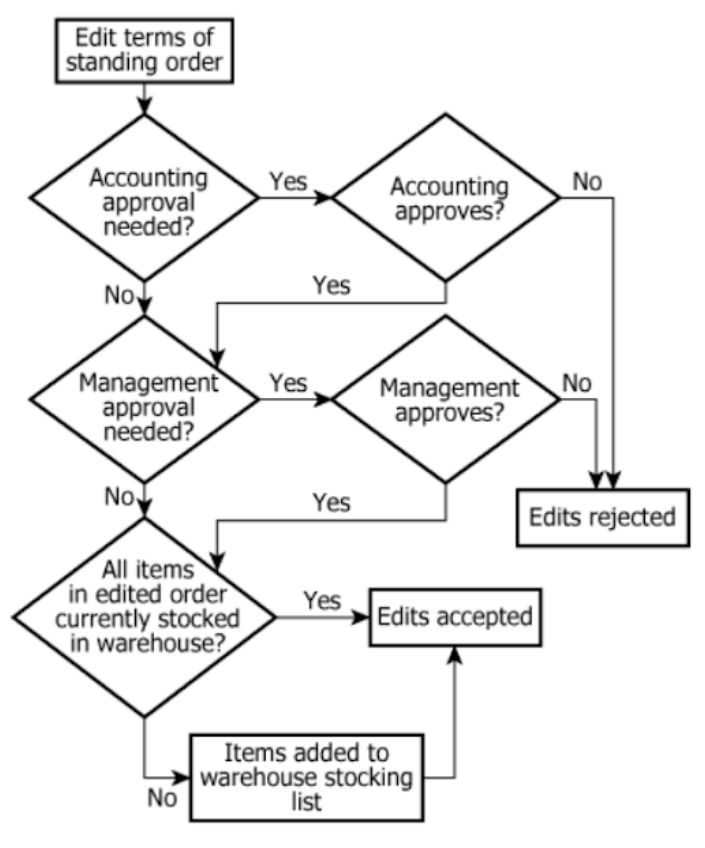
A certain wholesaler supplies goods on a regular schedule to various retailers. A retailer can choose to receive the same numbers and types of goods on a regular basis without having to submit a new order for each delivery using what is called a standing order. The flowchart represents all of the steps in the process for evaluating and accepting or rejecting a request to edit a standing order with the wholesaler. The process begins with "Edit terms of standing order."
Suppose that G is a group of requests evaluated using the process described in the information provided. Select from the drop-down menus the options to complete the statement so that it most accurately reflects the information provided.
| Text Component | Literal Content | Simple Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Business relationship | "A certain wholesaler supplies goods on a regular schedule to various retailers." | The wholesaler regularly delivers goods to retail stores. |
| Standing order definition | "A retailer can choose to receive the same numbers and types of goods on a regular basis without having to submit a new order for each delivery using what is called a standing order." | A standing order lets a retailer automatically get repeated deliveries with no additional orders. |
| Process purpose | "The flowchart represents all of the steps in the process for evaluating and accepting or rejecting a request to edit a standing order with the wholesaler." | The flowchart explains how edit requests are reviewed and either approved or denied. |
| Process entry | "The process begins with 'Edit terms of standing order.'" | Every review starts with someone requesting a change to their standing order. |
| Chart Component | Representation | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Decision points | Five diamonds (e.g., accounting approval needed?, approves?, management approval needed?, approves?, all items stocked?) | There are multiple possible checkpoints for each request and approvals are conditional. |
| Outcomes | Two endpoints: 'Edits rejected' and 'Edits accepted' | Every request is either fully approved or fully rejected by the end. |
| Warehouse stocking step | Box: 'Items added to warehouse stocking list' immediately before 'Edits accepted' | If approved and items aren't stocked, they're added to be stored in the warehouse before acceptance. |
| Branch logic | Yes/No arrows from decision points | The process follows branches: a 'No' at any approval leads to rejection, 'Yes' lets the request advance. |
| Process order | Approvals before stock check | Requests must get all approvals before final stock (warehouse) verification. |
Requests to edit a standing order must navigate multiple decision points, with specific approvals possibly required by accounting and management. All approvals must be granted before the system checks if the requested items are already stocked in the warehouse. If some approved items are not stocked, they are added to the warehouse stocking list before the edit is accepted. If required approvals are not obtained at any stage, the request is immediately rejected. Thus, only requests passing all relevant approvals and, if necessary, adding new items to stock, are accepted.
If each request in G [was approved by Accounting / was approved by Management / resulted in items being added to the warehouse stocking list], then it must have been the case that ...
... then it must have been the case that [some, but not all / all / none] of the requests in G included one or more items that were not currently stocked in the warehouse.
If every request in G resulted in items being added to the warehouse stocking list, then all requests in G must have included an item not currently stocked. This is the only outcome that guarantees this conclusion, as shown in the flowchart.
The questions are linked: the answer to the second blank depends on which flowchart outcome was chosen in the first. Only if all requests resulted in new items being added can we conclude all requests included at least one unstocked item.